What is Bipolar Disorder?
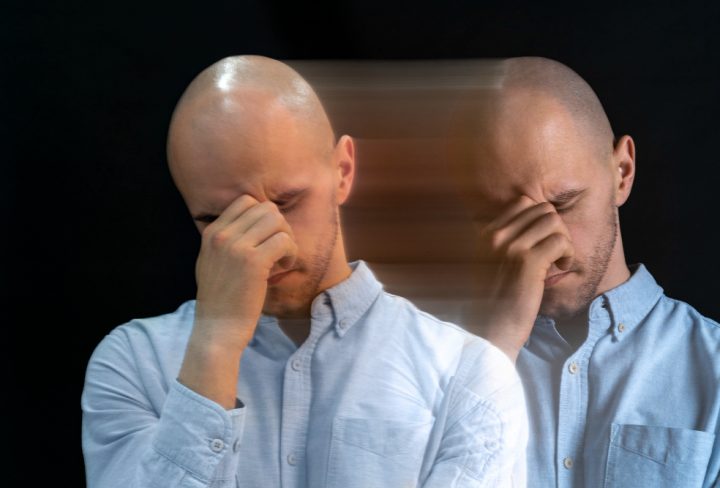
Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition that affects mood, energy, and activity levels. People with bipolar disorder often experience strong mood changes. These changes can shift from feeling very happy or “up” (mania) to feeling very sad or “down” (depression). Because these shifts can be severe, they can affect daily life. According to the World Health Organization, bipolar disorder affects millions of people worldwide. However, with the right support, many people manage their symptoms well.
Common Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
Recognizing bipolar disorder symptoms early can help with treatment. Symptoms usually fall into two main types: mania and depression. Sometimes, people may also have mixed episodes, where both types of symptoms appear together.
Additionally, symptoms can vary from person to person. If you notice these signs in yourself or someone else, it is important to seek help.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of bipolar disorder is not fully known, experts believe several factors play a role. For example, genetics can increase risk if a close family member has the condition. Brain structure and function may also be involved. In addition, stressful life events or trauma can trigger symptoms in some people. However, not everyone with these risk factors will develop bipolar disorder.
Because risk factors can vary, it is important to talk to a doctor if you have concerns.
How is Bipolar Disorder Diagnosed?
Many people wonder, “How is bipolar disorder diagnosed?” Diagnosis usually starts with a mental health professional. First, the doctor will ask about your symptoms, mood changes, and family history. Next, they may use special questionnaires or checklists. Sometimes, blood tests are done to rule out other health problems. However, there is no single test for bipolar disorder. Diagnosis is based on your symptoms and how they affect your life. Early diagnosis can help you get the right treatment sooner.
Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder
There are several bipolar disorder treatment options available. Treatment often includes a mix of medicine, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Because each person is different, your doctor will create a plan that fits your needs.
In some cases, hospital care may be needed for severe symptoms. However, most people can manage their condition with regular care and support.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Bipolar Disorder
Living with bipolar disorder can be challenging, but many people lead full lives. Here are some tips to help manage symptoms:
Because stress can trigger symptoms, finding ways to relax is also important. For example, try deep breathing, meditation, or gentle exercise.
Prevention and Early Intervention
While you cannot always prevent bipolar disorder, early intervention can make a big difference. If you notice mood changes or other symptoms, talk to a doctor right away. Early treatment can help reduce the impact of symptoms and improve quality of life. In addition, learning about the condition can help you spot warning signs sooner. Family members can also play a key role by offering support and encouragement.
Frequently Asked Questions
If you or someone you know may have bipolar disorder, consult a mental health specialist for personalized guidance.